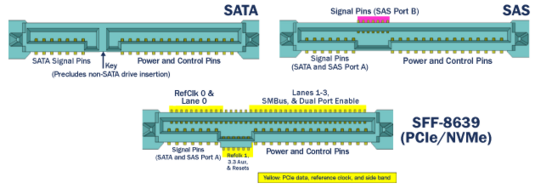
SSD
Solid-state drives (SSDs) come with a variety of connectors, connection protocols, underlying technologies and form factors. The primary types of SSDs are the 2.5”, M.2 (SATA & NVMe), NVMe PCIe and the U.2 (formerly SFF-8639) SSD, each offering distinct advantages and disadvantages.
| Type | Connector | Protocol | Technology | Form Factor | ETC. | Connector | Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M.2 SATA SSD | M.2 | SATA | SATA | M.2 | - 22 or 30mm wide
- 2280, 1630, 3030 |
0.6GB/s | |
| M.2 NVMe SSD | M.2 | PCIe | NVMe | M.2 | 8GB/s | ||
| 2.5" SATA SSD | SATA | SATA | SATA | 2.5" | 0.6GB/s | ||
| 2.5" U.2 SSD | U.2 (SFF-8639) | PCIe/SAS/SATA | NVMe | 2.5" | sff-8639 | 8GB/s | |
| PCIe Add-in-Card(AIC) SSD | PCIe | PCIe | NVMe | PCIe AIC
(Add in Card) |
8GB/s |
EDSFF
EDSFF stands for Enterprise and Data Center Standard Form Factor previously known as the Enterprise and Data Center SSD Form Factor is a family of SSD form factors for use in data centers[1]
Samsung's PM983 - NGSFF (also known as M.3 or NF1) form factor competes with EDSFF[2].
| Variation | Height | Length | Thickness |
|---|---|---|---|
| E3.S | 76mm | 112.75mm | 7.5mm |
| E3.S 2T | 76mm | 112.75mm | 16.8mm |
| E3.L | 76mm | 142.2mm | 7.5mm |
| E3.L 2T | 76mm | 142.2mm | 16.8mm |
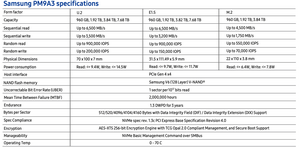
Samsung PM9A3 vs. Samsung PM983
PM9A3 offers better NAND and a new controller (V6 TLC and Elpis 8-channel, respectively) compared to the PM983’s V5 TLC NAND and Phoenix 8-channel controller[4]
PCIe 4.0 SSD
as of SAN JOSE, Calif., April 26, 2022, Solidigm introduced new series of SSD - D7-P5520 and the D7-P5620 - for high performance with zero tolerance for data errors. D7-P5520 (designed for read-intensive and light mixed workloads) and the D7-P5620 (designed for mixed workloads)[5].
Hothardware's performance benchmark shows competitive performance against competitors[6] in the market.
Reference
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enterprise_and_Data_Center_Standard_Form_Factor
- ↑ https://www.anandtech.com/show/13609/pcisig-warns-of-incompatibilities-between-m2-and-samsungs-ngsff
- ↑ https://www.snia.org/sites/default/files/SSSI/OCP%20EDSFF%20JM%20Hands.pdf
- ↑ https://www.compuram.biz/documents/datasheet/Samsung_PM9A3-m2.pdf
- ↑ https://news.solidigm.com/en-WW/213598-solidigm-introduces-the-industry-s-most-advanced-pcie-4-0-ssd-family-optimized-for-cloud-and-enterprise-workloads
- ↑ https://hothardware.com/reviews/solidigm-ssd-d7-p5520-data-center-nvme-review?page=2